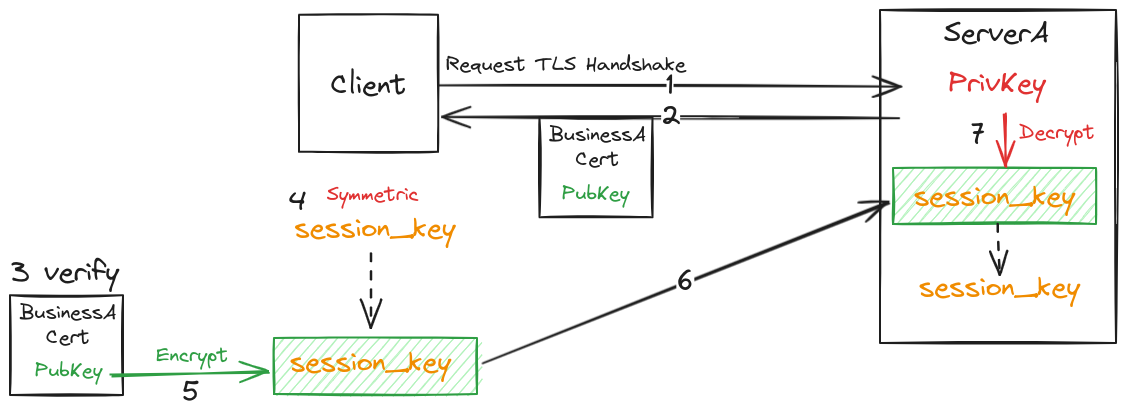
Public Key Infrastructure
-
Encryption
-
Symmetric
- Uses the same secret key to encrypt and decrypt the message

-
Asymmetric
- It deploys two keys, public key and private key
- a public key known by everyone and a private key known only by the owner/receiver
- a public key is used to encrypt the message and a private key is used to decrypt it or the other way around

-
-
Hashing
- A given known input must always produce one known output
- Once hashing has been done, it should be impossible to go from the output to the input
- Different multiple inputs should give a different output
- Modifying an input should mean a change in the hash

-
Digital Signature
- Encrypted hashed-data

-
PKI
-
Certificate Authorities
- Root CA
- CA/Intermediate CA
- Certificates
-
Certificate signed by CA
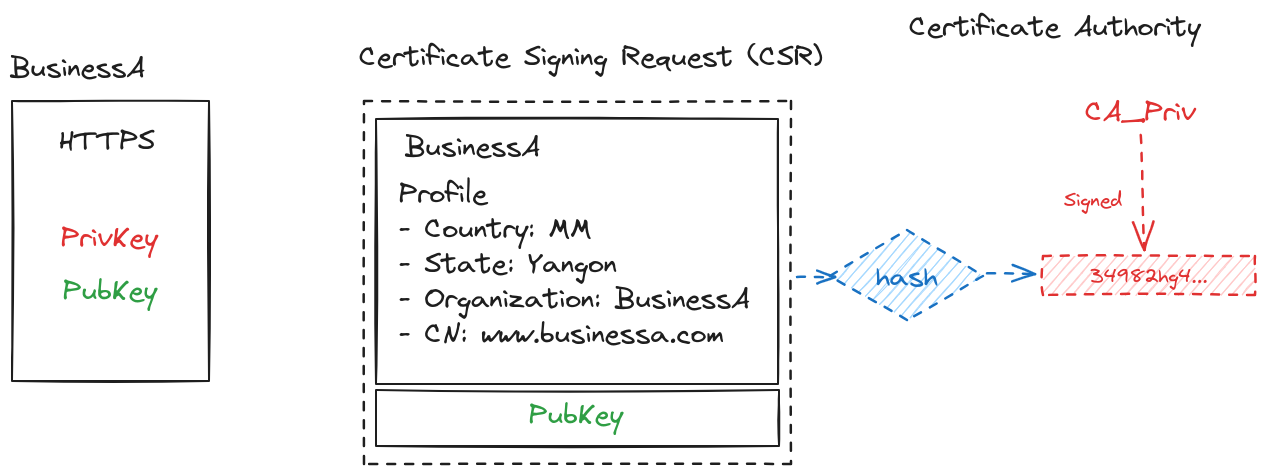
-
CA Certificate signed by Root CA
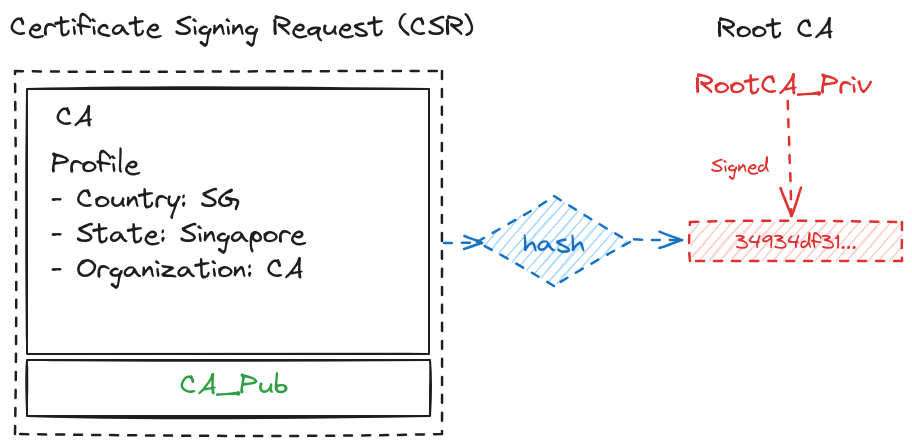
-
Root CA Certificate signed by Root Private Key
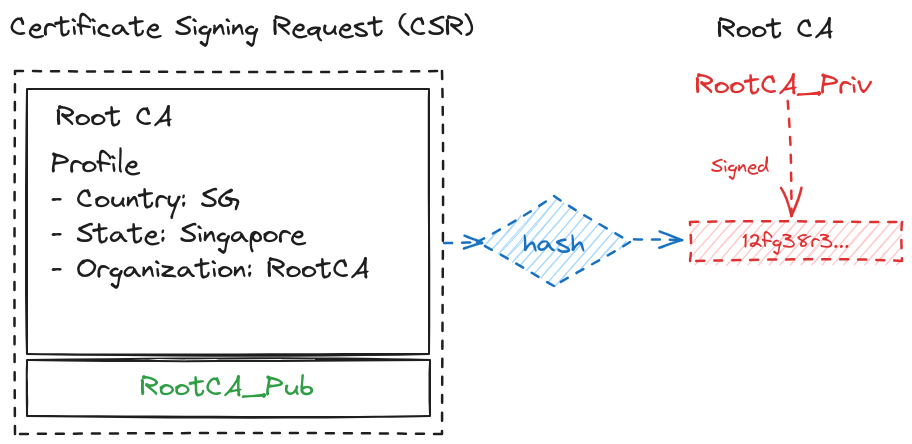
-
Full-chain
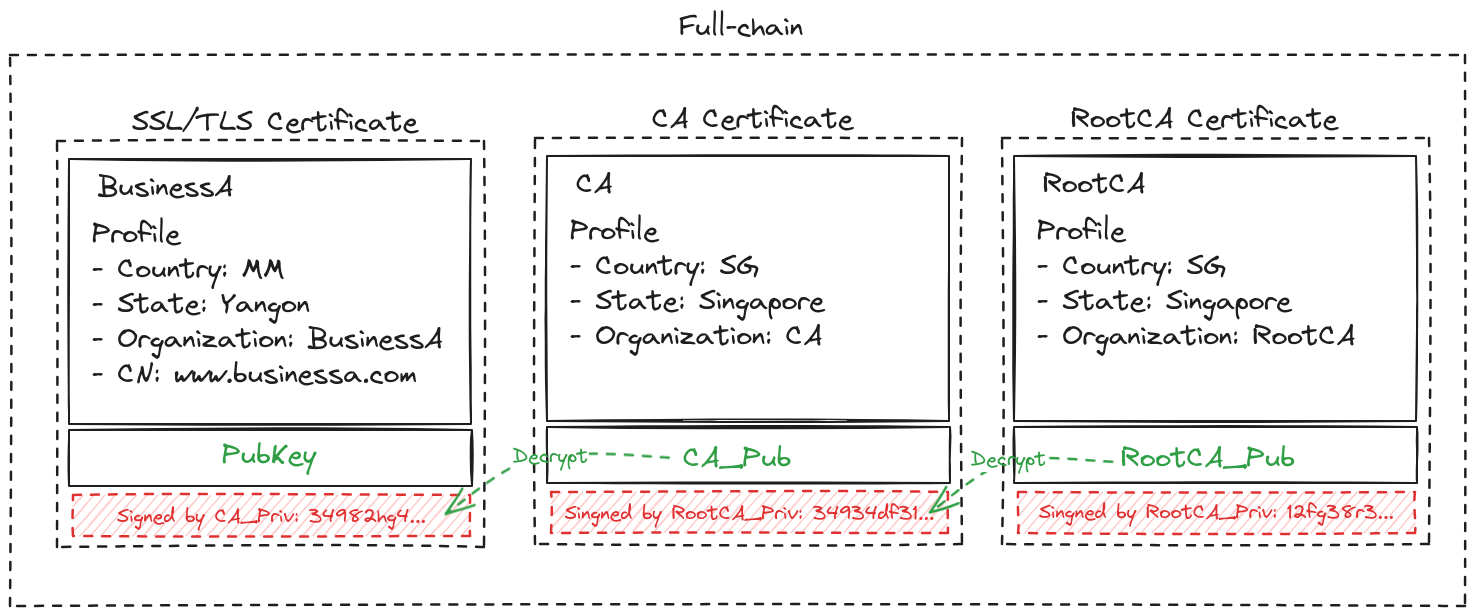
-
Self-signed Certificate
- Signing a certificate with own Private Key
-
CA-signed Certificate
-
Certificate which is verified and endorsed/signed by a CA
-
CA is verified and endorsed/signed by a Root CA
-
-
-
Securing HTTP
-
Cipher Suites
-
Key Exchange Algorithm
- RSA, DH, ECDH, DHE, ECDHE, or PSK
-
Authentication Algorithm
- RSA, ECDSA, or DSA
-
Bulk Data Encryption Algorithm
- AES, CHACHA20, Camellia, or ARIA
-
Message Authentication Code (MAC) Algorithm
- SHA-256, and POLY1305
-
Example:
-
Key_Exchange-Authentication-Cipher(Algorithm_Strength-Mode)-Hash/MAC
-
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
-
-
-
Key Exchange (RSA)
-
Lab: Exploring Cipher Suites
-
Client Side Ciphers
-
openssl ciphers -V 'ALL:eNULL'
-
-
Server Side Ciphers
-
nmap -sV --script ssl-enum-ciphers example.com
-
-
-
Certificate Format (X.509)
-
an International Telecommunication Union (ITU) standard defining the format of public key certificates
-
X.509 certificate binds an identity to a public key using a digital signature
-
Contains an identity (a hostname, or an organization, or an individual) and a public key
-
Base64
-
PEM - Privacy-Enhanced Email
- Extensions: .pem, .crt, .ca-bundle
- Base64 encoded DER files
-
PKCS#7 - Public Key Cryptography Standards
- Extensions: .p7b, .p7s
- Mostly used on Windows and Java Tomcat
- Cannot store private keys, only primary and intermediate certificates
-
-
Binary
-
DER - Distinguished Encoding Rules
- Extensions: .der, .cer
- a binary encoding format, rarely used outside of Windows
-
PKCS#12
- Extensions: .pfx, .p12
- can include the entire SSL certificate chain and key pair in a single file
- password-protected container
-
-
-
Lab: Nginx SSL/TLS Termination
-
Generating Self-signed certificate
-
Generate a Private Key
-
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
-
-
Extract a Public Key from the key pair
-
openssl rsa -in server.key -outform PEM -pubout -out public.pem
-
-
Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
-
openssl req -key server.key -new -out server.csr -subj "/C=MM/CN=server.example.com" -addext "subjectAltName = DNS: www.example.com, DNS: web.example.com"
-
-
Generate a Certificate by signing the CSR with its own Private Key
-
openssl x509 -signkey server.key -in server.csr -req -days 365 -out server.crt
-
-
Generate a Certificate without CSR
-
openssl req -key server.key -new -x509 -days 365 -subj "/C=MM/CN=server.example.com" -addext "subjectAltName = DNS: www.example.com, DNS: web.example.com" -out server.crt
-
-
One liner Self-signed certificate
-
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout server.key -x509 -days 365 -subj "/C=MM/CN=server.example.com" -addext "subjectAltName = DNS: www.example.com, DNS: web.example.com" -out server.crt
-
-
-
Signing a certificate with an own CA
-
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout ca.key -x509 -days 3650 -subj "/C=MM/ST=Yangon/L=Yangon/O=Know Your Linux/CN=KYL CA" -out ca.crt openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout server.key -x509 -days 365 -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -subj "/C=MM/ST=Yangon/L=Yangon/O=Know Your Linux/CN=*.example.com" -out server.crt
-
-
-
-
Troubleshooting Tips
-
Checking Certificate Expiry
-
openssl s_client -connect server.example.com:443 | openssl x509 -noout -dates -
openssl x509 -in server.crt -noout -dates
-
-
Viewing Certificate Info
-
openssl x509 -in server.crt -noout -text
-
-
Checking Private Key's integrity
-
openssl rsa -in server.key -check -noout
-
-
Matching with Private Key and SSL/TLS Certificate
-
openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in server.crt openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in server.key -
[ $(openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in server.crt) == $(openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in server.key) ] && echo Valid || echo Invalid
-
-
Checking supported TLS Version
-
openssl s_client -connect server.example.com:443 -servername server.example.com -tls1 openssl s_client -connect server.example.com:443 -servername server.example.com -tls1_1 openssl s_client -connect server.example.com:443 -servername server.example.com -tls1_2 openssl s_client -connect server.example.com:443 -servername server.example.com -tls1_3
-
-
-
Encrypting a file with SSL/TLS Certificate
-
openssl smime -encrypt -aes256 -binary -in file.txt -out file.enc -outform PEM server.crt openssl smime -decrypt -in file.enc -out decrypted_file.txt -inkey server.key -inform PEM -binary
-
-
Signing a file using a SSL/TLS Certificate and Key
-
openssl dgst -sha256 -sign tls_private_key.key -out file.sig file.txt openssl dgst -sha256 -verify server.crt -signature file.sig file.txt
-